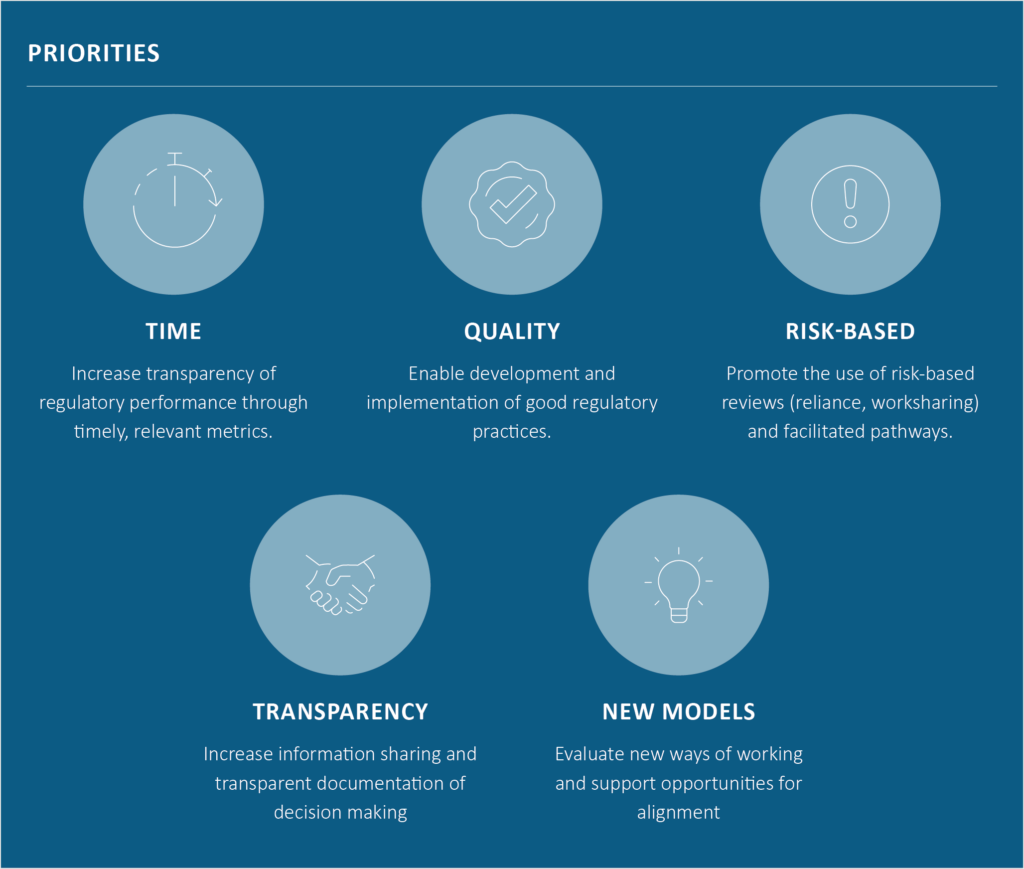
Regulatory Workstream
Goal: Provide a neutral forum for the evolution of the global regulatory environment by facilitating the advancement of regulatory science concepts, tools and policies that improve the effectiveness, efficiency and decision making of companies and regulatory agencies in the development of safe and effective medicines.